The generators are useful electrical equipment that rescues from power outages by supplying the power to your house’s appliance and keeps them working. So how to determine the size of the generator that you are going to need.
Table of Contents
How Do I Calculate My Power Needs?
For determining the size of the generator, calculate your power needs; this is the first step you will need to perform.
The heavy equipment in the house will have two power ratings, the starting watts, and the running watts consecutively. Follow these steps to get an estimate of the power needs of your appliances.

STEP-1
The first thing you will need to do is to make a list of every appliance you would like to be powered by the generator during the period of a power outage.
It can be AC, Refrigerator, Lights, fans, etc.
STEP-2
The second step is to calculate the power requirement of the appliances you have selected.
For that, you will need to consider the starting watts and running watts for all appliances. For the proper starting of some appliances, you will require more wattage at starting than running at a constant pace. Like, an air conditioner.
Running wattage is the required power so that appliances can keep working properly after the starting phase has faded.
Suppose some appliance in the house requires 1800 starting watts and 1400 running watts, which means the appliance will need 1800 watts at starting, and after that, it will work with the 1400 running watts.
When you are selecting a generator, both wattages need to be considered.
If you buy the generator with the 1700 starting watts and 1500 running watts, then the appliance won’t start because the generator isn’t capable of supplying the 1800 starting watts.
You can easily find these ratings in the owner’s manual. And to get the total power requirement, add the starting watts and running watts of all appliances individually.
STEP-3
After calculating the wattage of all the appliances, keep in mind to buy the generator that offers a little more power than actually required.
If the generator is of the same rating as appliances need, then the generator may suddenly stop its operation if there is a little overload. To prevent this from happening, it is better to have a generator whose rating is a little higher than your needs.
Besides, if the generator runs at the full load mode, it can significantly decrease its lifespan. Plus, the generator at full load produces much more noise.
So, it will be a good choice to buy the generator with a higher rating.
What is Running Watts and Starting Watts?
Running and starting watts both need to be considered when you want to buy the generators. So let’s see what these ratings are.

Starting Watts :
Generally, the appliances with an electric motor will need more power at the starting than when they are running.
The starting phase will be of around 2-3 seconds, and as the name suggests, the starting watts are the extra power needed at the starting of an appliance. These appliances contain inductive loads such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwave.
It is the maximum watts that a generator is capable of supplying for a limited time without damaging itself.
The appliances might have this rating written on them, but if it’s not there, you might want to take a look at the manual, or you may need to call the manufacturer.
Running Watts :
This is the rating that most of the appliances will have listed on themselves, and it is of most importance. Running watts are the continuous flow of power that needs to be supplied to the equipment to function properly.
Running watts are the maximum wattage that a generator can provide consistently to the appliances without damaging itself.
After a few moments of the peak watt supply, the device is started, and it will no longer require that peak wattage, but it requires fewer watts, which is the running watts.
Some appliances will only have running watts like bulbs and hot plates.
Difference Between Watt, Volt, and Amps
Watt, Volt, and Amps are units of electricity.
In the US, All electrical outlets supply a voltage of 120V, and for some heavy appliances, you get an option of 220V as well. Voltage determines the strength of the flow of current through the circuit.
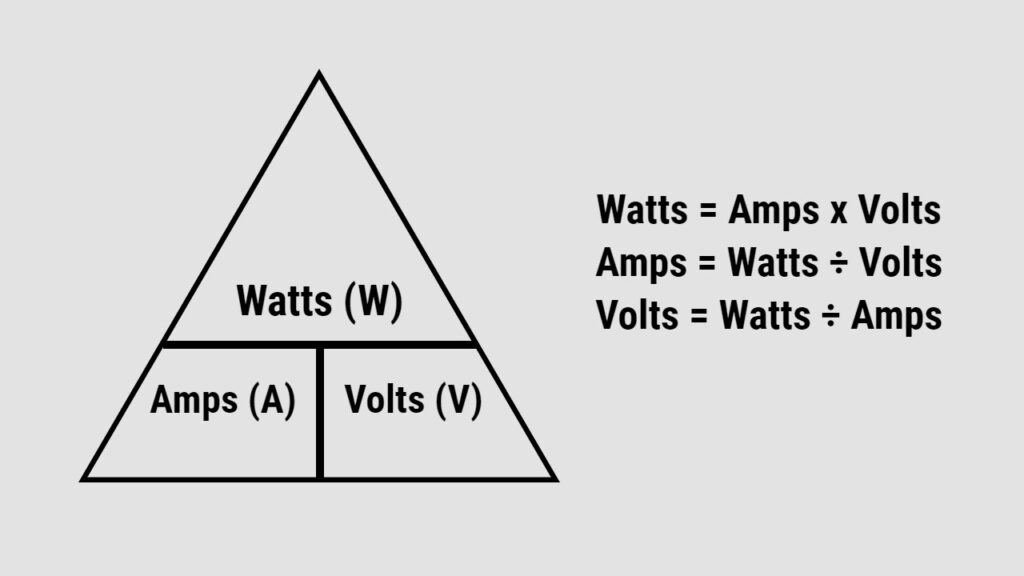
Generally, the power rating of any appliance is mentioned on the back of the label, and it is generally expressed as Amps (A) or watts (W).
Those are different units but are used to indicate the power consumed or supplied. There is a simple formula to calculate the running watts of any appliance if you know its rating in Amps. This formula will tell you how large a generator you will need.
Wattage = Amps x volts
Now suppose we want to find out the power for an appliance which draws 50 A from a 120 V outlet.
Then,
Wattage = 120V x 50A = 6000 Watts
This means that for continuous operation of that appliance, it will need 6000 running watts. Similarly, you can find the Amps if you know the wattage.
How Generator size is Measured?
The generator size is basically measured in terms of its power output and not the physical dimensions. Some people assume that the generators are sized based on their dimension, which is not entirely wrong, because coincidently, the generators with high power ratings have a bigger engine size, and less power output generators have a smaller size.
Generally, the size of the generators is mainly measured and determined based on the size of the house and the type of appliances you want the generator to supply the power.
The main consideration is the type of appliances you want to power; either you can power the whole house, or you can choose to supply only the essential equipment of the house. TVs, computers, refrigerators, lights are few appliances that you might want to run in a power outage; if so, then the small generator will do the job; thus, you will not need that expensive standby generator. But for more heavy application, these small generators will not work.
All the power needs of an average size house can be fulfilled by using a generator with a power output of 5000 to 7000 watts. The generator of this range supplies power to the house; you can easily run the refrigerator, freezer, lighting circuits, etc.
The generator for an RV of 3000 to 4000 watts can easily meet its energy demands.
Can I Use a Non-Inverter/large Generator to Power Sensitive Electronic Devices?
If we go with just the possibility, can the large generators be used to power the sensitive electronic equipment? The answer to that question will be Yes, you can.
But, we strongly suggest against that. Any modern electronic device like laptops or flat TVs will work very smoothly if the THD of the power supplied is below 3%. The power available to us from the electrical utility at the outlet in homes is clean, the THD of it almost always remains below 3%.
But that’s not the case with the large portable generators. However, the stationary generators are well capable of supplying that clean power, but the portable non-inverter generators just can’t do it.
They generate power that isn’t properly processed and contains spikes or surges, which can damage the processors of those electronic devices which work on low voltages.
So, if you rely on the power from large generators to supply your sensitive electronics, then your devices might get damaged after long-term use. Besides, there is a solution to this: the Inverter Generators, but they aren’t capable of supplying more power due to limited power-producing engine design.
Can I Power Whole-House Appliances with A Portable Generator?
It depends on the size of the house; if it’s a small house with few appliances and its wattage rating falls below the rating of the portable generator, then you can energize the whole house.
Besides, the large portable generators will have a THD of more than 3%, so there is a chance of the small electronics getting damaged, while the inverter generator supplies clean power, but they have a low output capacity, so you can only run a few appliances with it.
Generally, portable generators are available in the range of 10,000 to 15,000 watts, and these generators are cheaper than standby generators. They are capable of supplying the whole medium-sized house.
But, if you want a true whole-house generator, then we suggest you buy the standby generator with a rating of 16,000 Watts and higher.
Why is Getting the Right Size Generator Important?
As we have discussed, the size of the generator means its power output.
If you want to save some money by reducing the generator’s size but want to power the same number of equipment, then it won’t be good for anyone, not for you, the generator, or for the appliances you are powering.
If the generator is too small to power the appliances you want it to power, then it will overheat and automatically shut down by itself. That’s what modern generators do when there is an overload detected; they shut themselves down.
But if it overheats and keeps supplying the demanded power, then it will shut down after some time but not before inflicting some damage to the generator or your appliances.
Similarly, if you choose the generator which is too large to supply the load, then you will be paying more money for the power that you don’t need. Plus, the operating cost associated with large generators will be a bonus to your expenses.
From this, you can conclude that it is extremely important to choose the right size of generator for given load demand, and the selection of the right size generator can be made by 3 steps mentioned in the calculation of power needs. It is advisable to buy a generator that has a little higher rating than the power needs.
What are the Benefits of The Right Size Generator?
The right and proper size of the generator has many benefits besides avoiding the problems created if the generator is too small.
Reduces Failures
The small generators, which operate over their capacity sometimes, tend to fail, and that too frequently due to their overloading. The solution can be just to turn it back on, but it may get frustrating if you have to do it repeatedly.
Once you use the properly sized generator, you won’t have to worry about downtime; you can’t afford it, especially if you are working from home.
These failures can also be occurring due to something is broken inside, or the generator is used extensively for several years.
Long Lifespan
The generator requires a sizable amount of investment. You just can’t entertain the thought of having a short lifespan; you want the generator to last as long as it could.
But operating the generator at its full capacity reduces its lifespan drastically. So to make sure the generator doesn’t always run at the full load, you need a properly sized generator to ensure its long lifespan.
While some less expensive models might not make a dent in your pocket and can be replaced, but home generators are expensive, you can’t afford them to have a short lifespan.
Safety
The main concern of everyone when using a generator is the safety of the house and loved ones.
When the power requirement of the appliances is solely dependent on the generator, the power supplied to them should be sufficient, and that too without any mishap.
The generators should not create a short circuit or should not stop supplying the power unexpectedly; these can also be a safety concern in the cold of winter or the summer heat.
The generator of the right size avoids these happenings and supplies the needed power, making your home more comfortable.




